
Call for a free measure and quote:
0421 647 527
FLOORS2u


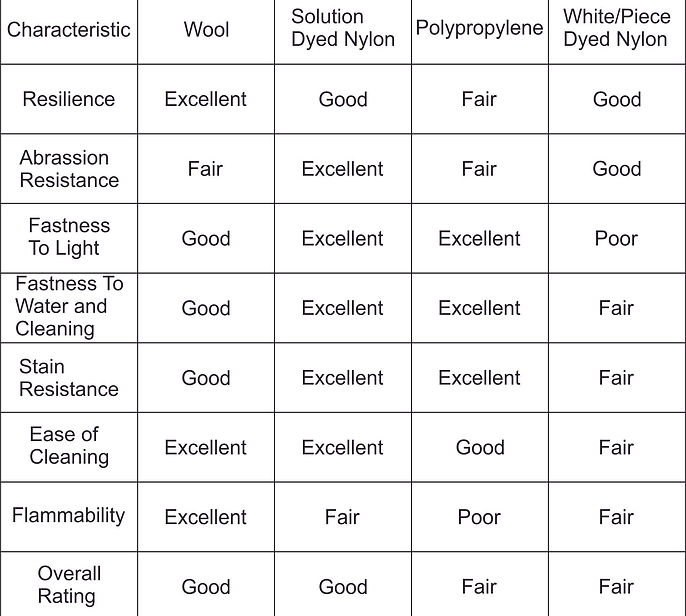
Carpet Attributes
CARPET FIBRES
Carpet fibre and its weight can make your carpet significally better quality. Different carpet fibres equal different looks. The most common types of fibres are wool, synthetics and wool/synthetic blends.
Wool definately sets the standard for all carpet types. The complexity of the fibre developed naturally to protect sheep in all weather conditions, makes it superior from the rest. Wool looks and feels simply fantastic.
WOOL FIBRES
Most suppliers use Solution Dyed Nylon (SDN), polypropylene and regular cost effective white nylon. Each fibre has its benefits and although all are synthetic, they have similar qualities. SDN is durable, strong yet flexible fibre that is colourfast and stain resistant as it is appropriately treated. Polypropylene is a hardy fatigue resistant fibre that is colourfast and inherently stain resistant. Polypropylene is the cost effective option over nylon.
SYNTHETIC FIBRES
Blends are created using a mix of wool and synthetic fibres in various percentages. The advantages of having a blend are reduced fuzzing and shedding which help maintain the carpets appearance for a long time. At the same time wool blends offer the beautiful feel and look of wool.
BLENDS
Carpet Fibre Characteristics
Carpet characteristics are those conditions characteristic of the yarn system and/or construction of the carpet. They are not considered as carpet defects or faults.
CHARACTERISTICS
Its perfectly normal for carpet to show minor (+/-10%) colour variation from the selling sample and/or variations between production runs. This is mainly due to carpet being manafactured in batches from dyeing the fibre through to the finished product. Manafacturers in Australia have very high standards for achieving consistency in colour.
TIP - Its best to view samples in home/residence or place of installation under as many different light conditions.
COLOUR VARIATION
All carpets graded by the ACCS must meet minimum standards for colour fastness. However carpet, like all other textiles, can fade if exposed to direct sunlight over a long period of time.
TIP - Use of blinds, curtains or exterior canopies will limit UV exposure.
FADING
Both matting and tracking of the pile are caused by foot traffic. In high usage areas and turning points. Placing rugs, mats and/or runners will aid with the prevention of tracking.
PILE DISTURBANCE
This is a phenomenon that can appear in any cut pile carpet. Its occurance is random and its causes are largely unexplained. It is also referred to as watermarking, pooling or puddling. A cut pile carpet that has shaded will show areas lighter or darker than the surrounding carpet pile. This variation is caused by the reflection of light from pile tufts which come to lay in different directions.
PERMANENT PILE REVERSAL/SHADING
Shedding describes the small fibres the carpet sheds in the first few weeks or months of use. Its most common in cut pile and in wool carpet. As the carpet settles the condition settles and becomes less noticeable.
TIP - Regular vacuuming usually reduces this problem.
SHEDDING
Fuzzing appears as fibre particles on the surface of carpet. Fuzzing is most apparent in areas where feet are shuffled such as under tables and in front of lounge chairs.
TIP - This can be corrected by a professional carpet cleaner shearing away the fuzz.
FUZZING
1 Vacuum your carpet once to twice a week
2 Treat spills immediately
3 Have your carpets professionally cleaned every 1-2 years
HOW TO MAINTAIN YOUR CARPET
THE ART OF FLOORING
"SERVING MELBOURNE SINCE 1999"